Cinderella proof that a new pair of shoes can change your life.
WHAT IS FOOT ABDUCTION BRACE?
As it was mentioned in the description of the PONSETI METHOD TREATMENT the Foot Abduction Brace (FAB) is a crucial element in the treatment of congenital clubfoot using Ponseti method. It is an orthopedic equipment that is used to maintain the correction which was obtained before. It means that the foot which is not fully corrected is not ready for the use of a brace! It also means that the brace does not treat the foot by itself but keeps the feet in the correct position. It is very important to understand this relationship between treatment and maintenance of correction.
When the brace is used correctly, the treatment effects are amazing and the chance of having healthy feet increases.
Many years of experience of Dr. Ponseti showed that the best results in clubfoot treatment are obtained when the feet are kept in the correct position (abduction + dorsiflexion). The experience of the doctors who followed him helped to clarify a little the specific “rules and guidelines”, thanks to which it is known how to navigate in the topic of bracing.
DESIGN
The design of foot abduction brace is not complicated. Each brace consists of the same components, independently from the place where it was made. However, these components should meet some conditions, because the correctness of the treatment depends on them at this stage. And if the brace does not meet these requirements, after some time, specific problems and regress of treatment can be seen.
A FAB consists of two shoes connected by a bar.
SHOES/ BOOTS
Boots which are used in FAB:
- have a straight form: it means that boots are not profiled inside: the right boot is good to the left foot and the left one is good to the right one;
- have the open toes: they provides not only ventilation but also allows toes to move freely;
- have a high heel counter: it supports the Achilles tendon and calf;
- they can be laced and strengthened with a leather (or synthetic) strap in the place where the foot flexes up and down. An additional strap keeps the foot in a good position in the boot. These are Markell shoes or similar ortotic products used around the world;
- they can also have three leather straps instead of lacing: sandal form. And these are Mitchell (Ponseti) boots;
- in the back part of the boot they have holes (or a hole) cut out so that it is possible to see the position of the heel inside;
- they can be attached to the bar with screws (in the Denis Browne bar) or the “quick clip” system (Mitchell and Dobbs bar).
BAR
The bar connects two boots to each other. It can be said in a nutshell. However, it is not just a simple piece of light metal. It has to enable the feet to the position of external rotation and it has to maintain dorsiflexion.
Setting the feet in the external rotation it is the first condition. It means that the feet are facing outward more or less. The appropriate bar allows smoothing setting of this parameter.
In the Denis Browne brace the boot is the most often attached to the bar with the screw and it is the boot which has a metal plate on the sole with drilled holes, where it attachs and tightens the bar with a screw. In the Mitchell and Dobbs bar the ends of the bar have drilled holes, which are hidden under a black circle (in the Mitchell bar) or a black and green circle (in the Dobbs bar) and the boot is attached to the bar with “quick clip” system, i.e. quick-connector . As a standard, the holes are drilled every 10° so the external rotation is set at 30°, 40°, 50°, 60° and not e.g. 34°, 45°, 53° etc.
Maintaining the dorsiflexion it is the second condition for design a proper bar. The foot must be held in permanent dorsiflexion by the bar to prevent shortening of the Achilles tendon, that the effects of the treatment are successful. This is important because clubfoot has a strong tendency to relapse. A strong, thick and wide Achilles tendon must be constantly stretched so that the child can stand and walk freely. Achilles tendon tenotomy removes the equinus position what causes that the foot can stand completely on the ground and allows the foot to move up and down. It is a very important movement, because it allows us to walk smoothly and load the foot correctly (and if it is properly loaded, the knee, hip and spine are evenly loaded). In order for the Achilles tendon not to shorten again (this is one of the features of the defect itself), it is necessary to keep it in constant, passive stretching.
Depending on the type of the bar, maintenance of the dorsiflexion is achieved in three ways:
- a well-made Denis Browne bar is bent along its entire width (the bar is bent towards from the child). This bend is: 10-15°
- Mitchell bar has bent ends (upward). The bend is 15° (although the US has Mitchell bars with a bend of 10°).
- in the Dobbs bar (Dobbs Spring Assist), springs perform the function of maintaining the dorsiflexion. Their bending varies between 10-15°. However, it happens that during the use of this bar, the springs lose their power and it happens that they fall. In addition, the child is able to deal with them in two ways: when the spring is too strong, the foot becomes maximally valgus. When the spring is weak and / or the child has a lot of strength, he can easily direct his foot down overcoming the power of the springs.
IMPORTANT
While there is no combination in the design of the Mitchell (Ponseti) bar (it is always the same), so it is in the construction of the Denis Brown bar, because in many courties it is manufactured locally by a given orthotic company. Unfortunately, the low knowledge of craftsmen often translates into a product of poor quality, what is directly related to the correctness of the treatment.
IF THE BRACE DOESN’T MEET THE ABOVE CONDITIONS,IT IS NOT USEFUL EQUIPMENT AND THE TREATMENT EFFECTS ARE VERY LITTLE OR EVEN A REGRESS LEADING TO RECURRENCE.
TWO WIDTHS
In order for the bar to fulfill its conditions that support the correction, it must be correctly positioned. In many publications the term “to the shoulder width” often appears. It seems necessary to systematize the concepts, because there is a great chaos and on its basis problems with the correct understanding of the issue arise.
The experience of doctors treating with the Ponseti method shows that the principles of correct bar positioning are unknown, although they should be common, especially for medical personnel dealing with the treatment of congenital clubfoot.
The basis is the width of the bar itself and secondly – setting the width of the bar to the width of the baby shoulders. Let’s look at these two widths.
BAR WIDTH
The bar width is the distance between the middle screws in the black circles. In the Mitchell bar it will be a black circle (similar to the Dobbs bar). In Denis Browne bar, it will most often be a metal plate attached to the bottom of the shoe, to which the bar is tightened with a screw. Thus, following this clue, bar width is measured from one middle screw to the other midlle screw. This is shown in the graphics below.
THE WIDTH OF THE BAR AFFECTS NOT ONLY ON THE COMFORT OF ITS USE,
BUT, ABOVE ALL, FOR CORRECT MAINTENANCE OF THE CORRECTION INCLUDING DORSIFLEXION,
WHAT AFFECTS DIRECTLY INTO THE TREATMENT EFFECTS.
The Mitchell bar is available in 3 sizes (in Polamnd in 4), the Dobbs bar in 2 sizes. Check our article about FAB WIDTH and see our experience with the ruler.
“ARM”/ SHOULDERS WIDTH
When asking parents what the “arm width” measurement means for them, the most common statement is that it is the distance from the end of the arm to the end of the arm. Yes that is true. The problem arises when we consider the correct medical terms.
- Arm to is the part of the upper limb located between the shoulder girdle (connected by the shoulder joint) and the forearm (which ends with the elbow joint).
- Shoulder is in other words a shoulder girdle, so it is a combination of the scapula, a collarbone (clavicle) and the joints accompanying them both on the right and left side.
In many sources you can find information that the width of the bar is equivalent to the width of the shoulders, e.g.: “The bar should be of the length between the child’s shoulders and should be bent to allow for 10-15° of dorsiflexion.” (“Bracing in the treatment of children with clubfoot: past, present, and future.” – Laaija Desai, Florin Oprescu, Andrew DiMeo, Jose Morcuende).
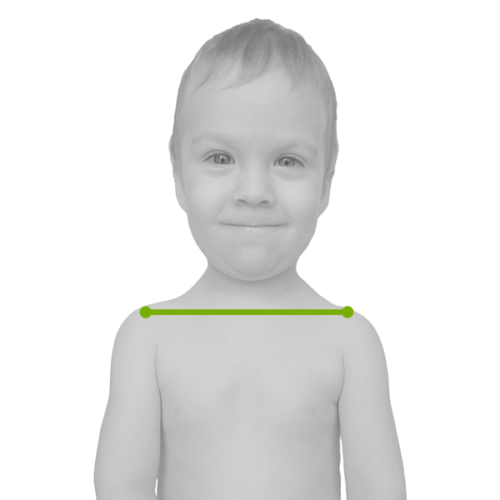
WIDTH TO THE WIDTH
As a Ignacio Ponseti Foundation, we take one of the directions in which the width of the bar is equal to the width of the baby’s shoulders, and this is the measurement taken from the front, as it does not take into account the convexity of the back.
THE BAR WIDTH SHOULD BE AS THE WIDTH OF THE SHOULDER MEASURED FROM ONE SHOULDER TO THE SECOND SHOULDER.
WHAT IS AFFECTED BY THE BAR WIDTH?
COMFORT
The width of the bar primarily affects the comfort of the child’s life. Too wide bar affects into its tolerance and hence a real treatment effect: it will be good or none. If we don’t like something and we don’t feel comfortable with it, we don’t want to use it. We try our best to avoid this by inventing a series of excuses, until at some point we give up using it. Everyone can predict the effect of such kind of treatment. Perhaps the following examples will help you to better understand this issue:
- Imagine that you have a malocclusion that causes not only health problems (e.g. inflammation of the temporomandibular joint or headaches), but also your teeth are crooked and it makes you smile reluctantly. You need to wear an orthodontic braces to achieve a specified health effect, but also a visual one. What do you think: would an orthodontic braces bought on AliExpress be a good solution for you? If the braces were not adjusted to your bite and its anomalies, being too big, too loose and badly profiled, what treatment effects would you get by using it? Would the inflammation go away or get worse? Would your head stop aching? Would such a braces be worn by you willingly? Probably not. You would notice a great difference if after a month of wearing such braces, you would start using the correct orthodontic braces.
- Imagine you have vision problems. You see that … you can’t see correctly. Do you buy glasses at the poor market or do you do firstly the research, and then you order the appropriate glasses to be made in an appropriate optical shop, where after they are made, they are also adjusted to you (axis alignment, temples bending, nose pads bending)? Improperly fitted glasses cause that you still cannot see or see out of focus and that you may have a headache from unsuitable lenses or pressure the frames.
- Imagine you are skiing but the skis are not well suited to your height. Yes, skiing is possible, but it is definitely not comfortable. If the skis are too short, the risk of losing control on the slope is high, because they are unstable, very maneuverable, they are unable to support the skier and vibrate quite strongly. On the other hand, skis that are too long are clunky, hard to maneuver and spring strongly. In both cases, skiing with this kind of skis require putting more force than skiing with fitted skis. Our joints feel it after a whole day of “fighting” with the equipment, when they start to ache while resting. It is easy then for injuries and fractures to happen, e.g. overload fractures, which will effectively eliminate us from the slope to…the hospital.
CORRECTION
When the bar is wider, the heel in the boot does not fit well to the boot insert and “hangs” – the heel goes up and this is an occurrence which is not good. When the heel hangs in the air, the Achilles tendon becomes shorter. Each change in the position of the joints in relation to each other is compensated elsewhere in our body.
CHANGES AND CONCLUSIONS
When our Foundation began to popularize the set of the bar to the width of the shoulders, we noticed many benefits that confirmed our belief that this is the right way.
- children tolerate the bar better (the increase in tolerance of this equipment increased from 40% to 87%)
- dorsiflexion increases and remains at an average level of about 20°
- the foot fits better in the boot – the “holes” in Mitchell boot are filled – the heel is good in the insole and does not hang over it
- the condition of the foot is not getting worse
- physical activity is not limited – children became more active and, for example, rolling over from the back to the tummy became easier (because the width of the bar does not block them) and it happened at a similar time as for their healthy peers (and often even faster)
- hips and knees are not overloaded with excessive width
- in more difficult periods of life, e.g. growth and developmental spurts, teething or feverishness, children tolerate the bracing time more gently than with a wider bar
- the number of skin complications, such as pressure sores or wounds has also decreased – they occur less frequently
- due to the elimination of poor equipment and due to the fact that the bars are tolerated better and used longer according to a specific scheme (bracing protocol) – the number of unnecessary operations and surgical interventions has decreased definitely and significantly. And that is very good news!
The direction which we chose, we tested firstly on our own children. They were the most perfect settings and observations “testers”.
EXTERNAL ROTATION
After correctly adjusting the bar width, the next parameter to be set is the external rotation of the feet. And as in the case of ignorance of setting the width correctly, the occurrence is exactly the same here.
Generally, this parameter should be set only by a doctor. Taking into account the correctness of the previously applied plaster casts, the condition of the foot after removing the last cast and the degree of correction which was obtained, he should set the degree of external rotation. However, the occurrence of “automation” very often takes place here, so how as in the book, publications, scripts it is written that the clubfoot is to be set at 60-70°, it is set this way, without taking into account many factors that have already been mentioned. It’s a mistake.
If the doctor really knows the Ponseti method in its extent, he knows well that the degree of external rotation of the feet is set exactly like in the last plaster cast. It means that if the last plaster cast (before FAB) was in the so-called hypercorrection (abduction up to about 60-70° in 10-15° dorsiflexion at the same time) it is true – the abduction can be set to 60°, as stated by most scientific sources. These parameters are only used when the treatment is perfectly. If the last plaster cast did not have much abduction, the bar is set up in the same way as the plaster cast.
Example:
If the last plaster cast (the one after tenotomy – if it was done) had only 20° of abduction, when the child starts to use the brace, the boot abduction should also be 20°. And it should be increased gradually so that all soft structures inside the foot have time to stretch slowly and evenly. Abduction should finally reach 60° after a few / several weeks.
If the last cast had 40° of abduction, the boot abduction in the brace should also be 40 °. And it should be increased gradually so that all soft structures inside the foot have time to stretch slowly and evenly. Abduction should finally reach 60° after a few / several weeks.
Yes, we are talking about “standard” clubfeet, so those that most children have. ATYPICAL AND COMPLEX FEET have their own rights when it comes to setting the correct external rotation. And the doctor needs to know that.
60° OR 70°?
- an excessive overload of the hip
- the uneven stretching of individual muscles
- the excessive external tibial torsion (in the future, this is reflected in the child’s knees pointing outwards and is walking like Charlie Chaplin, with the feet too much outwards)
- the excessive valgus of the calcaneus, what is the straight way to real and non-physiological flat feet.
IF YOU HAVE ANY DOUBTS THAT THE CLUBFEET EXTERNAL ROTATION IN THE BRACE IS SET CORRECTLY,
CONTACT AN EXPERIENCED PONSETI DOCTOR OR WRITE TO US.
CAN THE DEGREE OF FEET AEXTERNAL ROTATION CHANGE DURING THE TREATMENT?
Yes. It can be changed many times as necessary. The most common reasons for changes are:
- sudden discomfort in usage of the brace by children around 2 years old – it is caused by the increasing tension of the periosteum due to the growth spurt (the periosteum is very nerved) – this is often manifested by the pain in the legs, grabbing the knees or feet, nervousness. Excessive external rotation of the foot (and thus also the shin bones) causes the periosteum to stretch. Often, changing the derotation by 10° less (yes, so little) reduces this problem. Of course, this is not a long-term change.
- „tibial torsion” – torsion of the tibia, what is related to the natural biomechanics of the lower limb: the greater the derotation is, the worse it is getting, causing discomfort. Tibial torsion should be checked by a doctor in an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computer Tomograph) examination, sometimes with the help of an X-ray examination (in specific X-rays views).
- excessive valgus of the heel in the foot, which can have many reasons (e.g. articular-ligament laxity). Then the bar is set “down” by 10 ° most often
- overcorrected foot does not require abduction at 60°: it requires much less
- positional clubfoot does not require a huge derotation – 30° is enough
- atypical and complex clubfeet – which start at 30° (complex) or 40° (atypical) degrees of derotation increased every few to several weeks to finally reach 60°.
YEARS AND HOURS
When Dr. Ponseti was writing his book and when Ponseti method began to make wider circles after many years of hiding, embracing many children’s feet and making them functional, it was determined that a FAB should be used for 2 to 4 years. Lately, knowledge about clubfoot and the Ponseti method has developed extremely – more and more interesting studies and publications are being written. Doctors around the world who treat with the Ponseti method believe that the longer the brace is used (in terms of years), the risk of relapse is lower.
Knowledge moves forward, but some things remain the same, guaranteeing success in treatment and reduction of invasive and unnecessary surgeries. Some doctors are working on standardizing the duration of use of the brace in relation to the each type of foot to determine how long a brace should be used in particular cases.
MINIMUM
The longer the brace is used, the risk of RELAPSE is lower.
LONGER?
As important as the length determined by the number of years, is the usage of the brace when it comes to the hours. It matters how many hours the brace is used during the day.
The time of using the FAB should be adjusted individually to the patient, based on his age, frequency of relapses related to reaching this age, end of the correction, condition of the foot, general predisposition.
Example:
The number of hours of bracing will be longer for a newborn that has been corrected within the 4-week compared to older children who are already walking after correction has been achieved.
However, even in this individual plan there is a general framework which doctors who treat with Ponseti method around the world adhere to. However, very often we meet two unbalanced directions.
We take a position of PONSETI INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION (PIA) – an association of doctors, medical professional and all those who spread the correct knowledge about the Ponseti method.
Therefore, we use the scheme proposed by Dr. Jose Morcuende, so the slow reduction of “bracing” hours. It is a balanced enough scheme in terms of maintaining the correction to prevent relapse and the child motor development and is also relatively well thought out and supported by the experience of doctors. And we notice its measurable results primarily on our own children and those we observe in the group of parents.
The bracing protocol describes the number of hours that a child should spend with the brace in relation to the total time of usage given in months and the reduction in that time. Of course, the protocol can be changed by a qualified doctor who is familiar with the Ponseti method.
DOCTOR JOSE MORCUENDE
is a pediatric orthopedic surgeon that specializes in clubfoot, hip disorders, tumors, fractures, and a number of other pediatric orthopedics diagnoses. Dr. Morcuende received his medical education and training from the University Autonoma of Madrid with an additional residency in Orthopedic Surgery here at University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics. Dr. Morcuende was a close colleague of Dr. Ignacy Ponseti. He spent many years with him observing his work at the University Hospital in Iowa, learning the details of the method, teaching others how it should be applied correctly. Extraordinary passionate. He devoted many studies and publications to the clubfoot. He is a member of many medical organizations and the PRESIDENT of PONSETI INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION.
The protocol is worked out to keep the clubfoot in a correction through the brace and at the same time not to limit the child natural activity. You might say there are two “protocols”. They take into account the age of the child at the time of starting the usage of a FAB.
THE AGE OF A CHILD UP TO 8-9 MONTHS
Most corrections are achieved around 2-3 months of child age. It means that around this time they begin their journey with the foot abduction brace. So they use the protocol for children up to 8-9 months of age. Sometimes it happens (and you need to be fully aware of this) that a relapse may occur and the re-treatment will be needed. If the baby achievs correction till 9 months of age, he continues to follow the protocol for babies up to 8-9 months. It is quite logical: most of the time a small child spends passively, what means that the brace can be safely used a little bit longer. When the activity appears and when it is dominant: the hours of bracing are reduced.
THE AGE OF A CHILD ABOVE 9 MONTHS
If your child starts the treatment or repeats it for any reason at the age of 8 months or more when he starts bracing, he will use a different protocol. It is related to the relatively well-developed activity of the child. Often children around 9 months old start to stand, some try to walk. Nature can not be stopped: children will cope with almost any obstacle or limitation, finding their own way for them. However, having this activity in mind, you need to find a balanced way to keep the correction of the foot.
THE ADVANTAGES OF THE PROTOCOL
- good maintenance of correction, reducing the risk of relapse;
- slowly reducing the hours of using the brace, taking into account the increasing activity of the child;
- low risk of rejection and intolerance of the brace due to the fast hourly jump: 23/24 hours -> 8 hours … 5 hours … 11 hours …
IMPORTANT
The foot abduction brace should be used not less than 10 hours a day. If the baby is small, he sleeps during the day: a brace should be used at each nap. Taking naps has the same meaning as sleeping at night.
Why?
Babies fall asleep hard and deep very quickly. Deep sleep makes the whole body relax: it is not active – muscles, tendons and ligaments do not work because they are not set in motion by the brain. Each relaxation of the foot during sleep requires the use of a brace, even when the child sleeps 10 minutes…
PSYCHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF USING THE BRACE
The above content has focused on what is the “external” elements of the treatment: the width of the bar, its proper fit to the baby’s shoulders, etc. However, there remains something that is a key element at this stage of treatment. It is your head, the Parent!
Very often, when parents share with us, they say that “the brace limits the child” or “he will not be able to sleep with it” or “my child suffers from the brace”. Sometimes parents bring such news from physiotherapists, pediatricians, other parents. Often these parents are also attacked by their own families in order to “not to tire the child”, “why do you put it on for him/her? Though, he has nice feet.” e.t.c.
We understand all your concerns and at the same time we want to assure you, the Parent, that your deep awareness and your in – depth understanding of the usage of this orthopedic equipment, as well as your attitude, are the basis for the good treatment of your child. We can guarantee you that you are not alone on this way – we walk ahead of you as practitioners, but also as careful and precised observers and we guarantee that if the brace is appropriate and your attitude towards it is optimistic, this phase of the treatment runs more efficiently, even when there are occasional difficulties.






















